Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), a remarkably versatile material, has revolutionized numerous industries, from packaging to construction. Its unique properties, including being lightweight, offering excellent insulation, and its cost-effectiveness, make it a preferred choice. This article delves deep into the world of EPS shape moulding, exploring the intricacies of the EPS molding process, the critical role of the mold, and the sophisticated EPS shape molding machine technology that brings complex designs to life. If you’re involved in manufacturing, particularly in sectors that utilize EPS foam, understanding this technology is paramount. We’ll explore how these molding machines work, the benefits of EPS, and what to look for when investing in this crucial equipment. This comprehensive guide is worth reading because it will equip you with the knowledge to optimize your production, enhance product quality, and make informed decisions, especially if you’re like Mark Thompson, a company owner looking for reliable and efficient EPS machinery.
What Exactly is Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Why is it a Manufacturing Marvel? (Understanding EPS)
Before diving into the molding process itself, it’s essential to grasp what EPS actually is. Expanded Polystyrene, often referred to by its genericized trademark Styrofoam in some regions, is a rigid and tough, closed-cell foam. It is usually white and made of pre-expanded polystyrene beads. The journey of EPS begins with tiny spherical polystyrene beads that contain a blowing agent, typically pentane. When heat, in the form of steam, is applied to these beads, the blowing agent causes them to expand significantly, up to 40-50 times their original volume. This pre-expansion step is critical. These expanded beads are then allowed to mature and cool before being introduced into a mold.
The marvel of EPS lies in its structure: approximately 98% air and only 2% polystyrene. This composition is what gives EPS its remarkable properties: it’s incredibly lightweight, yet possesses excellent shock absorption and excellent insulating properties. These characteristics make EPS a popular choice across many industries. Its versatility allows it to be molded into an almost limitless array of shapes and sizes, from simple blocks for insulation to intricate custom packaging for fragile items. The ability to produce large quantities of EPS products efficiently further cements its status as a manufacturing cornerstone. As a factory owner specializing in EPS machinery, I’ve seen firsthand how this material transforms production lines.
The manufacturing process of expanded polystyrene is relatively straightforward but requires precise control, which modern molding machines provide. Understanding the fundamental nature of EPS – these tiny beads transforming into robust foam structures – is the first step to appreciating the sophistication of the shape moulding technology. The durability and adaptability of EPS mean it can be engineered to meet specific performance criteria, whether for thermal insulation, protective packaging materials, or even structural components in some applications.
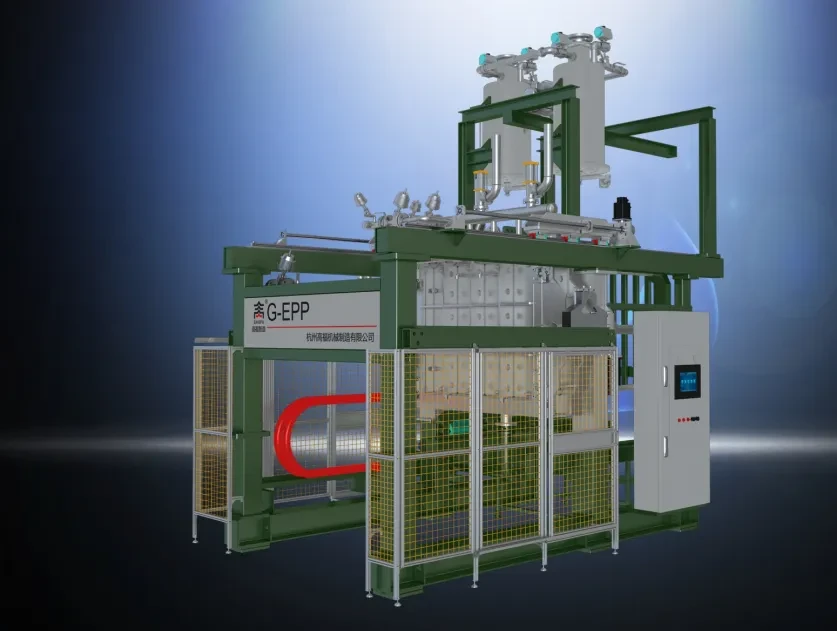

The Core of Creation: How Does the EPS Shape Moulding Process Work? (EPS Molding Process, Moulding Process)
The EPS molding process is a fascinating journey where loose EPS beads are transformed into solid, shaped foam products. It all begins after the pre-expansion stage, where the raw polystyrene beads have already increased in size. These conditioned, expanded beads are then conveyed into a mold cavity. The mold, which is custom-designed for the desired product shape, is a critical component. Once the mold is filled, the moulding process truly begins. Steam is again introduced, this time into the closed mold. This heat and pressure causes the expanded beads to soften and expand further and fuse together, perfectly taking the shape of the mold cavity.
After the fusion, the mold must be cooled. This is typically done by circulating water through channels within the mold or by a vacuum cooling system. Proper cooling is essential to stabilize the molded foam part and allow it to be handled without distortion. Once the part is sufficiently cool and rigid, the mold opens, and the finished EPS product is ejected, often with the help of ejector pins or air pressure. This cycle – fill, steam, cool, eject – is repeated, allowing for the efficient production of numerous identical parts. The precision of this EPS molding process ensures high product quality and consistency.
The entire EPS molding process is carefully controlled by the shape molding machine. Modern machines can automate most, if not all, of these steps, from bead filling to part ejection. This automation not only speeds up production but also ensures uniformity and reduces the chances of human error. The ability to accurately control steam pressure, heating times, cooling times, and fill density is paramount to achieving the desired properties in the final EPS product. The efficiency of this moulding process makes it a cost-effective solution for various industries.
Spotlight on the Star Player: What is an EPS Shape Molding Machine? (EPS Shape Molding Machine, Shape Molding Machine)
An EPS shape molding machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed specifically for the manufacturing process of EPS foam products. This machine is a specialized piece of industrial hardware that takes pre-expanded EPS beads and transforms them into various shapes and sizes according to the mold installed within it. Think of it as the heart of any EPS production line. These molding machines are engineered to handle the critical stages of the molding process: filling the mold with beads, applying steam for expansion and fusion, cooling the mold, and ejecting the finished product.
The complexity of an EPS shape molding machine can vary. Some are basic, requiring more manual intervention, while others are highly automated, integrated systems. Key components typically include a bead filling system, a steam chamber and distribution system, a mold clamping unit, a cooling system (often vacuum-assisted), and an ejection mechanism. The control system, usually a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), is the brain of the shape molding machine, allowing operators to set and monitor parameters like steam time, cooling time, and pressure to ensure optimal product quality.
As a manufacturer, we at YouLi Machinery offer a range of EPS Shape Moulding Machines that cater to diverse production needs. These molding machines are built for durability and efficient production, incorporating energy-saving features and user-friendly interfaces. The goal is to provide our clients, like Mark Thompson, with reliable equipment that can produce large volumes of high-quality EPS products consistently. The right shape molding machine is an investment that directly impacts productivity and profitability.
The Unsung Hero: Why is the Mold So Crucial in EPS Molding? (Mold, EPS)
While the shape molding machine provides the power and control, the mold is arguably the most critical element in determining the final form and quality of an EPS product. The mold, often made from high-grade aluminum, is a precision-engineered tool that defines the exact shape, size, and surface finish of the molded foam part. It consists of two halves – a core and a cavity – which come together to create the space where the EPS beads will expand further and fuse together. The design and construction of the mold are paramount.
A well-designed mold ensures uniform filling of EPS beads, efficient steam distribution for complete fusion, and effective cooling to solidify the part quickly. Intricate details, sharp corners, and complex geometries can all be achieved with a precisely crafted mold. The material of the mold is also important; aluminum is often preferred for its excellent thermal conductivity, which helps in both the heating and cooling phases of the moulding process, and its relatively lightweight nature, which facilitates easier handling and faster cycle times. The surface finish of the mold directly translates to the surface finish of the EPS product.
Investing in a high-quality mold is essential for any EPS manufacturer. A poorly designed or cheaply made mold can lead to a host of problems, including incomplete fills, inconsistent density, surface imperfections, and difficulty in ejecting parts, all of which compromise product quality and slow down production. The mold is not just a shaping tool; it’s an integral part of the heat exchange system within the EPS molding cycle. Therefore, careful consideration of mold design, material, and craftsmanship is vital for successful EPS shape moulding. The better the mold, the better the final EPS item.
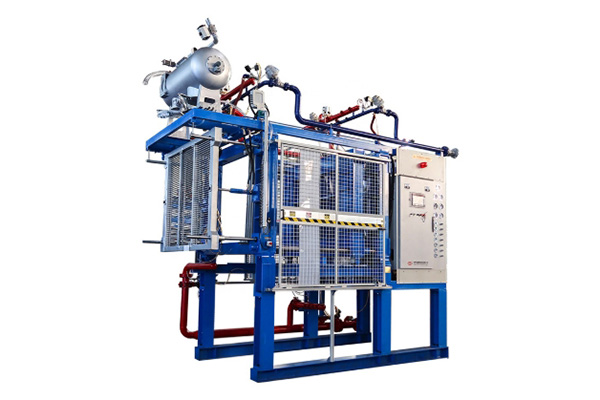

From Tiny Beads to Tangible Products: A Step-by-Step Look at EPS Molding (EPS Molding, Bead, Polystyrene Beads)
The journey of an EPS product from raw material to finished item involves several key steps in the EPS molding process. It’s a transformation that showcases the unique properties of polystyrene beads.
- Pre-expansion: This is the initial stage where raw polystyrene beads, containing a blowing agent, are exposed to steam in a pre-expander machine. The heat causes the beads to expand significantly, reducing their density. This step is crucial for achieving the desired final density of the EPS product. The size of the expanded bead is carefully controlled.
- Aging/Maturing: After pre-expansion, the expanded beads are typically stored in large silos for a period (usually 12-48 hours). During this time, the beads cool down, residual pentane and water vapor escape, and air diffuses into the bead cells, stabilizing their internal pressure. This maturation process is vital for ensuring dimensional stability and good fusion in the subsequent molding process.
- Mold Filling: The conditioned, expanded beads are then pneumatically conveyed from the silos to the hopper of the EPS shape molding machine. From the hopper, they are injected into the mold cavity using specialized fill guns. The goal is to fill the mold completely and uniformly.
- Fusion (Steaming): Once the mold is filled, it is securely closed, and steam is injected into the mold chamber. The heat and pressure from the steam cause the EPS beads to soften and expand further and fuse together, forming a solid, homogenous foam structure that takes the exact shape of the mold.
- Cooling: Immediately after fusion, the mold and the newly formed EPS part must be cooled rapidly. This is usually achieved by circulating cool water through channels in the mold walls or by applying a vacuum, which also helps remove residual steam and aids in dimensional stability. Efficient cooling reduces cycle times and prevents deformation of the EPS product.
- Ejection: Once the EPS part has cooled sufficiently and solidified, the mold opens, and the finished product is ejected. This can be done using ejector pins, air blasts, or robotic arms, depending on the complexity of the part and the level of automation.
- Post-Production (Optional): Depending on the application, the molded EPS parts might undergo further processing, such as drying, cutting (using an EPS Cutting Machine), printing, or assembly.
This systematic EPS molding process allows manufacturers to produce large quantities of consistent, high-quality EPS products efficiently. Each step is critical, and the shape molding machine plays a pivotal role in controlling these parameters.
What are the Key Advantages of Using EPS in Your Products? (Benefits of EPS, Lightweight)
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) offers numerous advantages, making it a popular choice across a wide spectrum of applications and various industries. Its unique combination of properties provides both functional and economic benefits. As someone deeply involved in the EPS machinery industry, I regularly see how these benefits translate into real-world success for manufacturers.
- Lightweight: This is perhaps the most recognized benefit. Being approximately 98% air, EPS is incredibly lightweight, which reduces transportation costs, makes handling easier, and is ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as packaging and buoyancy aids.
- Excellent Insulating Properties: EPS has a low thermal conductivity due to its closed-cell structure, which traps air. This makes it an excellent insulating material for buildings (walls, roofs, floors) and for temperature-sensitive packaging, helping to maintain desired temperatures and save energy.
- Shock Absorption: The cellular structure of EPS also provides exceptional shock absorption capabilities. This is why it’s extensively used for packaging fragile items like electronics, appliances, and glassware, protecting them from damage during transit and handling.
- Versatility and Customization: EPS can be molded into virtually any shape or size, allowing for intricate details and custom designs. This versatility is invaluable for creating bespoke packaging solutions, architectural moldings, and specialized components. The shape moulding process is key to this.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to many other materials with similar properties, EPS is relatively inexpensive to produce. The raw materials are affordable, and the manufacturing process, especially with efficient molding machines, is highly productive, leading to lower unit costs. This cost-effective nature is a significant draw.
- Durability and Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Despite being lightweight, EPS offers good compressive strength and durability. It can withstand considerable loads and impacts without permanent deformation, making it suitable for a variety of structural and protective applications.
- Moisture Resistance: EPS is highly resistant to moisture. It does not readily absorb water, which helps prevent mold growth and maintains its insulating properties even in damp conditions.
- Hygienic and Non-Toxic: EPS is non-toxic, odorless, and does not support fungal or bacterial growth, making it safe for food packaging and other sensitive applications.
- Recyclable: EPS is 100% recyclable. It can be reprocessed into new EPS products or transformed into other useful materials like clothes hangers, park benches, or even as a component in other plastics. This aspect is increasingly important for environmentally conscious businesses.
These benefits of EPS collectively contribute to its widespread adoption and continued growth in many industries. The ability to produce large volumes of EPS products with consistent quality further enhances its appeal.
Choosing Wisely: What Features Define a High-Quality EPS Foam Shape Molding Machine? (EPS Foam Shape Molding Machine, Molding Machines)
Investing in an EPS foam shape molding machine is a significant decision for any manufacturer. To ensure you get the best return on your investment and consistent product quality, it’s crucial to look for specific features that define a high-quality machine. As a manufacturer of these molding machines, I advise clients like Mark Thompson to consider the following:
- Robust Construction and Durability: The machine frame and components should be made from high-grade materials, ensuring long-term durability and reliability even under continuous operation. A well-built machine minimizes downtime and maintenance costs.
- Advanced Control System (PLC): A user-friendly and precise PLC system is essential. It should allow for easy programming and adjustment of all critical molding process parameters, such as steam pressure and duration, vacuum levels, cooling times, and fill speeds. Look for systems that offer recipe storage for different mold types.
- Efficient Steam and Vacuum Systems: The steam system should provide quick and uniform steam distribution within the mold. An efficient vacuum system is crucial for rapid cooling, reducing cycle times, and improving part quality by removing moisture and stabilizing the EPS beads. Energy-saving designs for these systems are a big plus.
- Mold Compatibility and Quick Changeover: The shape molding machine should be compatible with a range of mold sizes and designs. Features that facilitate quick mold changes, such as hydraulic clamping systems and standardized connections, can significantly reduce downtime between production runs of different EPS products.
- Precise Filling System: The system for filling the mold with EPS beads must be accurate and consistent. Look for machines with advanced fill guns and sensors that ensure the mold is filled optimally for uniform density and complete fusion.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern EPS foam shape molding machines should incorporate energy-saving technologies. This includes efficient motors, optimized steam and vacuum usage, and good insulation to reduce heat loss. Lower energy consumption directly translates to lower operating costs.
- Safety Features: Comprehensive safety features are non-negotiable. This includes emergency stops, safety interlocks on doors and guards, pressure relief valves, and clear warning systems to protect operators and prevent damage to the machinery. Compliance with international safety standards (e.g., CE marking) is important.
- Automation Capabilities: The level of automation can vary. High-quality machines often offer options to automate bead feeding, part ejection, and integration with downstream equipment like conveyors and EPS Stacking Machines.
- Ease of Maintenance and Availability of Spare Parts: The machine should be designed for easy access to components for routine maintenance. Furthermore, ensure that the manufacturer can provide reliable after-sales service and readily available spare parts. This is a key concern for buyers like Mark.
By prioritizing these features, manufacturers can select an EPS shape molding machine that not inbvestment but also a cornerstone for producing high-quality EPS foam products efficiently and reliably.
The Future is Automated: How Does Automation Enhance EPS Shape Moulding? (Automate, Efficient Production)
Automation is increasingly playing a pivotal role in the EPS shape moulding industry, transforming how EPS products are manufactured and significantly enhancing efficient production. For businesses looking to scale up, improve consistency, and reduce operational costs, adopting automated solutions in their EPS molding lines is becoming less of a luxury and more of a necessity. As a factory specializing in EPS machinery, we’ve seen a growing demand for automated systems. These systems can range from automating individual tasks on a shape molding machine to fully integrated production lines.
One of akey areas where automation brings substantial benefits is in material handling. Automated systems can manage the conveying of expanded beads from silos to the EPS shape molding machine, ensuring a consistent supply without manual intervention. After the molding process, robotic arms or automated conveyors can eject and transfer the finished EPS parts to the next stage, such as drying, cutting, or packaging. This not only speeds up the workflow but also reduces the risk of damage to the delicate foam products that can occur with manual handling. For instance, an Automatic EPS Block Conveyor can seamlessly integrate into a larger automated system.
Furthermore, automation within the EPS shape molding machine itself leads to greater precision and consistency. Automated controls for steam, cooling, and cycle times ensure that each EPS part is produced under identical conditions, leading to higher product quality and reduced scrap rates. Modern molding machines often feature PLCs that can store multiple recipes for different molds and products, allowing for quick changeovers with minimal operator input. This ability to automate complex sequences and adjustments minimizes human error and allows skilled labor to focus on oversight and quality control rather than repetitive tasks. The integration of sensors and data logging in automated systems also facilitates better process monitoring and optimization, contributing to overall efficient production and proactive maintenance.
Versatility in Action: What are the Common Applications of EPS Shape Moulding? (Applications of EPS, Packaging)
The versatility of EPS (Expanded Polystyrene), coupled with the precision of the shape moulding process, has led to its adoption in a vast array of applications of EPS across numerous various industries. Its unique combination of being lightweight, providing excellent insulation properties, and offering superior shock absorption makes it an ideal material for many uses. The ability to mold EPS beads into various shapes with intricate details means that custom solutions are readily achievable.
One of the most well-known applications of EPS is in packaging. It’s extensively used for packaging fragile items such as electronics (TVs, computers, appliances), glassware, and medical equipment. Custom-molded EPS foam inserts provide a snug fit, protecting goods from damage during shipping and handling. The epp foam packaging shape moulding also offers similar benefits for applications requiring higher resilience. Another major sector is construction, where EPS serves as an effective thermal insulation material for walls, roofs, and floors, contributing to energy efficiency in buildings. It’s also used in geofoam applications for lightweight fill in civil engineering projects.
Beyond these, EPS shape moulding finds its way into consumer goods, such as bicycle helmets, anchild car seats, where its impact absorption is critical for safety. It’s used for making disposable food containers, cups, and coolers due to its insulation and hygienic properties. In horticulture, EPS seed trays and propagation pots are common. The marine industry uses EPS for buoyancy aids, floats, and even as core material in small boat construction. The list is extensive and continues to grow as designers and engineers find new ways to leverage the benefits of EPS. The ability of the EPS shape molding machine to produce large quantities of these diverse products in a short time is a key driver of its widespread use.
Sustainability Matters: Is EPS an Environmentally Conscious Choice? (Environmentally Friendly, Recyclable)
The environmental profile of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is often a topic of discussion, and it’s important to look at the facts. While concerns have been raised about its persistence in the environment if littered, EPS itself has several characteristics that can contribute to a more sustainable approach, especially when managed responsibly throughout its lifecycle. One of the key positive aspects is that EPS is 100% recyclable. Modern EPS recycling machine technology allows used EPS foam to be reprocessed and transformed into other useful materials or even back into new foam products.
From a resource perspective, EPS is about 98% air and only 2% polystyrene, meaning it uses relatively little raw material to create a large volume of product. Its lightweight nature also translates to lower fuel consumption during transportation compared to heavier alternatives, reducing its carbon footprint in the logistics chain. The excellent insulating properties of EPS contribute significantly to energy savings in buildings, reducing the need for heating and cooling, which in turn lowers greenhouse gas emissions. This operational energy saving over the lifespan of a building can far outweigh the energy used in the EPS manufacturing process.
However, the challenge lies in establishing effective collection and recycling infrastructure. As an EPS machinery manufacturer, we see growing interest in recycling solutions, such as EPS compactors and melting machines, which reduce the volume of EPS waste and make it more economical to transport for recycling. It’s crucial for the industry, consumers, and municipalities to work together to improve recycling rates. When EPS is properly recycled, it becomes a valuable resource rather than waste, making it a more environmentally friendly option. The focus should be on responsible use, collection, and ensuring that EPS is channeled into appropriate recycling streams.
Partnering for Success: Selecting the Right EPS Machinery Manufacturer for Your Needs (Industry, EPS Products)
Choosing the right manufacturer for your EPS machinery, whether it’s an EPS Pre-expander Machine, EPS Block Moulding Machine, or a sophisticated EPS Shape Moulding Machine, is a critical decision that directly impacts your business’s efficiency, product quality, and long-term profitability. For company owners like Mark Thompson, who are knowledgeable but may lack deep technical expertise in the machinery itself, finding a reliable partner is paramount. As a factory owner, Allen, based in China and exporting globally to the USA, North America, Europe, and Australia, I understand the key concerns: machine performance, reliability, production capacity, automation level, energy consumption, and, crucially, after-sales service and support.
When evaluating potential suppliers for your EPS molding machines, look beyond just the initial price. Consider the manufacturer’s experience in the EPS industry and their reputation. Do they specialize in EPS and EPP foam machinery? Do they have multiple production lines, indicating capacity and expertise? A good manufacturer will offer a range of equipment used in the entire EPS lifecycle, from pre-expansion to recycling. They should be able to provide insights into the best machinery configuration for your specific EPS products and production volume. Ask about the availability of spare parts and the process for obtaining them – this is often a pain point for buyers.
Furthermore, communication and support are vital. Inefficient communication can lead to misunderstandings and delays. A responsive sales team and, more importantly, a strong technical support team are essential. Inquire about installation assistance, operator training, and troubleshooting support. Certifications like CE marking indicate compliance with international safety standards. At YouLi Machinery, we prioritize transparent communication and robust after-sales service because we understand that our success is tied to our customers’ ability to produce large quantities of high-quality EPS products without interruption. We aim to be more than just a supplier; we strive to be a long-term partner in your EPS manufacturing process.
Key Takeaways to Remember:
- Understanding EPS: Expanded Polystyrene is a lightweight, versatile foam made from expanded polystyrene beads, offering excellent insulation and shock absorption.
- The Molding Process: EPS shape moulding involves filling a mold with EPS beads, applying steam to expand further and fuse together, then cooling and ejecting the part.
- EPS Shape Molding Machine: This specialized piece of equipment is central to the manufacturing process, controlling the molding cycle.
- Critical Mold: The mold design and quality are paramount for producing accurate and high-quality EPS products.
- Benefits Galore: EPS is cost-effective, durable, moisture-resistant, and offers versatility for various industries, especially packaging.
- Machine Features: Look for robust construction, advanced controls, efficiency, safety, and automation in an EPS foam shape molding machine.
- Automation is Key: Automation enhances efficient production, consistency, and reduces labor costs in EPS molding.
- Wide Applications: EPS is used in packaging materials, construction insulation, consumer goods, and more.
- Sustainability: EPS is recyclable, and its insulating properties contribute to energy savings, making it a potentially environmentally friendly choice with responsible management.
- Choosing a Partner: Select an EPS machinery manufacturer based on experience, product range, support, and a commitment to quality, addressing concerns like those of Mark Thompson.
Post time: 05-12-2025