In the world of packaging, construction, and various industrial applications, foam materials are widely used for their insulating properties, lightweight nature, and ability to protect products during shipping. Among the most common types of foam are polyethylene (PE) and expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam. Understanding the differences between these two materials is crucial for selecting the right foam for specific needs, especially in industries that rely on Foam EPS machines for production.

Understanding PE Foam
Polyethylene (PE) foam is a closed-cell foam material made from polyethylene, a versatile thermoplastic polymer. PE foam is known for its resilience, flexibility, and excellent cushioning properties, making it ideal for a wide range of applications, from packaging to automotive parts.
Key Characteristics of PE Foam:
- Durability and Flexibility: PE foam is highly durable and flexible, allowing it to absorb shocks and impacts effectively. This makes it a popular choice for packaging fragile items, as it provides a protective barrier against damage during transportation.
- Water and Chemical Resistance: One of the standout features of PE foam is its resistance to water and chemicals. This property makes it suitable for applications in damp or harsh environments, such as marine and automotive industries.
- Insulation Properties: PE foam is an excellent insulator, both thermally and acoustically. It is often used in construction for insulation purposes, helping to maintain temperature control and reduce noise in buildings.
- Lightweight and Easy to Handle: The lightweight nature of PE foam makes it easy to handle and transport. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in industries where weight reduction is a priority, such as in packaging and automotive applications.
Understanding EPS Foam
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam is another type of closed-cell foam, made from polystyrene beads that are expanded and fused using heat and steam. EPS foam is commonly used in packaging, insulation, and construction due to its lightweight and rigid structure.
Key Characteristics of EPS Foam:
- Rigidity and Structural Strength: EPS foam is more rigid and structurally strong compared to PE foam. This makes it ideal for use in applications where a firm and stable material is required, such as in building insulation or protective packaging for electronics.
- Excellent Insulation: Like PE foam, EPS foam is also an excellent insulator. Its closed-cell structure traps air, providing high thermal resistance. EPS is commonly used in construction as insulation panels, helping to improve energy efficiency in buildings.
- Cost-Effective: EPS foam is generally more cost-effective than PE foam, making it a popular choice for large-scale applications where budget constraints are a consideration. Its affordability does not compromise its effectiveness in providing insulation and protection.
- Environmental Concerns: EPS foam has faced criticism due to its environmental impact. While it is recyclable, the recycling process can be challenging, and improperly disposed EPS can contribute to environmental pollution. As a result, there is a growing interest in finding sustainable alternatives or improving recycling methods for EPS.
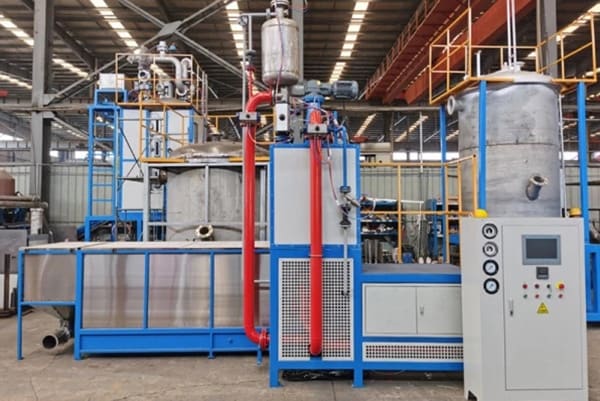
Foam EPS Machines: The Role in Manufacturing
Foam EPS machines are specialized equipment used to produce EPS foam products. These machines play a critical role in the manufacturing process, allowing for the efficient production of EPS foam in various shapes and sizes. Foam EPS machines work by expanding polystyrene beads and molding them into desired forms, such as packaging materials, insulation panels, or other products.
The efficiency and precision of Foam EPS machines make them essential for industries that require large quantities of EPS foam. By automating the production process, these machines help reduce waste, improve product consistency, and lower production costs.
Key Differences Between PE and EPS Foam
While both PE and EPS foam are widely used, they differ in several important aspects:
- Flexibility vs. Rigidity: PE foam is flexible and resilient, making it ideal for cushioning and protective packaging. In contrast, EPS foam is rigid and structurally strong, suitable for applications requiring firm support.
- Water Resistance: PE foam is highly resistant to water and chemicals, while EPS foam, though somewhat resistant, is not as robust in this regard.
- Cost: EPS foam is generally more cost-effective, making it a preferred choice for large-scale applications. PE foam, while more expensive, offers superior flexibility and durability.
- Environmental Impact: Both foams have environmental considerations, but EPS foam faces more scrutiny due to recycling challenges. Efforts to improve Foam EPS machine technology are ongoing to address these concerns.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between PE and EPS foam is essential for making informed decisions in various industries. While PE foam offers flexibility, durability, and superior water resistance, EPS foam provides rigidity, structural strength, and cost-effectiveness. The choice between the two often depends on the specific application, budget, and environmental considerations. As technology advances, particularly in the development of Foam EPS machines, the future may bring more sustainable and efficient solutions for foam production and use.
Post time: 08-16-2024